The Impact of Handicrafts on Sustainability: Creating with Awareness

The Impact of Handicrafts on Sustainability
Handicrafts have evolved far beyond mere artistic hobbies; they stand at the forefront of sustainable development. The artistic creation of handicrafts often emphasizes eco-friendly practices, significantly contributing to waste reduction and resource conservation. Crafts such as knitting, pottery, and woodworking not only serve as creative outlets but also play a vital role in promoting environmental responsibility.
One of the profound benefits of engaging in handicrafts is the reduction of carbon footprint. Unlike mass-produced goods that require extensive machinery and energy, handmade items typically involve lower energy consumption. For instance, a handmade ceramic pot utilizes far fewer resources than a large-scale factory-produced version. This shift towards more sustainable practices is crucial as consumers become increasingly aware of their environmental impact.
In addition to ecological benefits, handicrafts also support local economies. By buying handmade products, consumers often contribute directly to their communities, helping to foster job creation and economic resilience. For example, artisans selling their crafts at local farmers’ markets or craft fairs not only showcase their talents but also invigorate local commerce. This dynamic encourages a circular economy where money remains within the community, benefitting all involved.
Furthermore, many artisans prioritize the use of sustainable materials. A growing number of craftsmen opt for natural, biodegradable, or recycled inputs, aligning their practices with modern environmental goals. For instance, many knitters today utilize organic cotton or wool sourced from ethical farms, while woodworkers might use reclaimed wood, giving new life to discarded materials. Such choices not only beautify our homes but also minimize the ecological impact typically associated with conventional manufacturing processes.
Handicrafts encapsulate unique cultural heritage, making them a tool for awareness and appreciation of traditional skills. Participating in these artistic activities cultivates a mindset geared towards sustainable consumption, encouraging individuals to prioritize quality over quantity. As consumer consciousness rises, so does the demand for responsibly made products.
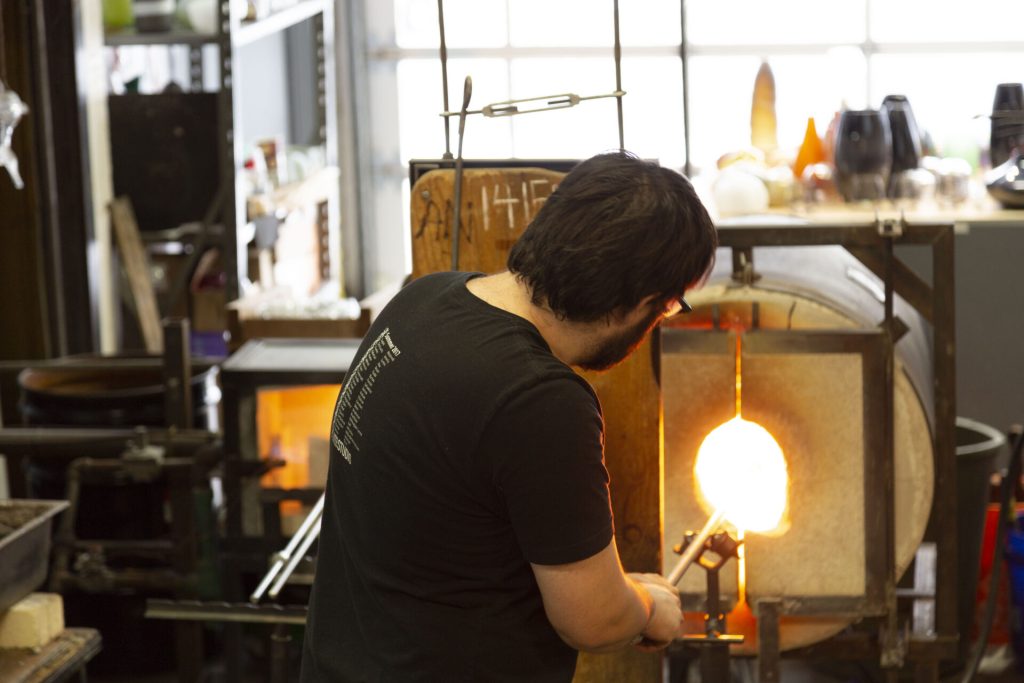

As we delve deeper into the impact of handicrafts on sustainability, it becomes increasingly clear that these activities are not merely creative pastimes; they are essential components of the ongoing fight for a healthier planet. Embracing handicrafts can fundamentally reshape our relationship with consumption and the environment, inviting us to create with thoughtful intention and a commitment to sustainability.
DISCOVER MORE: Click here to learn about the evolution of crafting
Connecting Craftsmanship and Environmental Stewardship
The relationship between handicrafts and sustainability extends beyond eco-friendly practices; it cultivates a deeper understanding of our environmental responsibilities. Delving into the artisanal world reveals a myriad of benefits that enrich both individual creators and society as a whole. The act of creating handmade items fosters a vital connection to materials and processes, profoundly influencing consumers’ choices and their impact on the planet.
One of the most compelling aspects of handicrafts is the shift toward using local resources. Artisans are increasingly sourcing materials from within their communities, minimizing the impact associated with transportation and logistics. By doing so, they not only reduce carbon emissions but also support local vendors and small-scale producers. For instance, artisans who use locally sourced clay for pottery are not only crafting unique pieces but are also contributing to local economies and preserving regional traditions.
Moreover, the mindfulness embedded in handicraft creation promotes an awareness of waste. Many craftspeople embrace upcycling, transforming discarded materials into beautiful new products. For example, textile artists may repurpose old clothing into quilts or unique fashion items. Such practices not only save materials from ending up in landfills but also inspire consumers to rethink their relationship with waste. By choosing to buy or create handmade goods, individuals disrupt the cycle of overconsumption often seen in fast fashion or mass-produced home décor.
Handicrafts also play a critical role in education and community engagement with sustainability. Through workshops and classes, artisans can impart valuable skills that encourage participants to embrace sustainability in their own lives. These programs often focus on:
- Teaching sustainable practices: Encouraging techniques that utilize less energy and resources.
- Promoting the use of natural materials: Highlighting the benefits of biodegradable or recycled inputs.
- Instilling respect for craftsmanship: Emphasizing the value of time, effort, and skill in creating handmade items.
This educational aspect not only enhances the craft community but also broadens the appeal of sustainability to a wider audience. Participants, inspired by their experiences, may carry these lessons into their daily lives, fostering a shift towards more responsible consumption practices.
Additionally, as consumer awareness grows, so does the demand for artisanal products that reflect ethical sourcing and sustainability. This shift is not merely a trend; it signifies a fundamental change in how individuals view their purchasing decisions. By choosing handicrafts over mass-produced items, consumers signal their support for sustainable production methods and the artisans dedicated to preserving our planet.
In summary, handicrafts serve as a beacon of hope in the quest for a sustainable future. They illuminate the path toward mindful consumption and showcase how artistic expression can bridge the gap between tradition and environmental stewardship. Embracing the craftsmanship of skilled artisans enables individuals to make conscious choices that resonate deeply with the values of sustainability, ultimately leading to a more harmonious coexistence with nature.
| Advantage | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Cultural Preservation | Handicrafts embody unique cultural heritage, allowing communities to maintain their traditions while promoting sustainable practices. |
| Eco-Friendly Materials | Crafting often involves using natural materials, which decreases dependency on mass-produced, environmentally harmful goods, highlighting sustainable resource use. |
The intersection of handicrafts and sustainability reveals a powerful narrative of environmental responsibility and social impact. As artisans utilize available resources responsibly, they create products that not only appeal to eco-conscious consumers but also reflect a commitment to preserving their surroundings. Through techniques passed down generations, these artisans create items that have a story and a purpose, allowing consumers to connect more deeply with their purchases.Moreover, the economic advantage of supporting local craftsmen cannot be overlooked. By choosing handicrafts, consumers directly contribute to the livelihoods of artisans, promoting economic sustainability. This dynamic bolsters local economies, reinforcing the community’s circular economy, where resources are reused and waste minimized.In a world increasingly focused on sustainability, recognizing the contributions of handicrafts to environmental conservation expands our understanding of responsible consumerism. As more people become aware of this impact, the demand for handmade items that embody these principles will likely continue to grow, encouraging a shift towards more conscious living.
DIVE DEEPER: Click here to unlock the power of your words
Handicrafts as Catalysts for Cultural Preservation
The impact of handicrafts extends beyond sustainability in environmental practices; it also plays a pivotal role in preserving cultural heritage. As globalization continues to shape consumer behavior, many traditional crafting techniques risk fading into obscurity. However, dedicated artisans and communities actively work to safeguard these art forms, ensuring that cultural identities do not vanish along with them.
In the United States, for example, the revival of indigenous crafting methods, such as basket-weaving or pottery, can be seen within numerous tribes. These artisans not only create stunning works of art but also embed stories, traditions, and values into their creations. By passing down skills through generations, they promote not only sustainability but also stewardship of cultural narratives that enrich communities. Programs like the National Endowment for the Arts fund initiatives that encourage such practices, fostering local identity and cohesion.
Economic Empowerment through Handicrafts
Handicrafts also offer profound economic benefits, creating opportunities for artisans who may not have access to mainstream markets. This economic empowerment is crucial in areas economically disadvantaged or overlooked by larger industries. By tapping into the growing market for sustainable and ethical products, artisans can achieve a sense of financial independence while upholding their traditional skills.
For instance, platforms like Etsy and Fair Trade organizations allow artisans to showcase and sell their unique creations to a global audience. These sales generate income that can uplift families and communities, exemplifying a business model where artisans can thrive. In 2022, the global handicrafts market was valued at approximately $717 billion and is expected to grow as awareness of sustainable products increases. This growth reflects a shift in consumer preferences toward supporting local artisans and fair labor practices.
Fostering Community Connections through Collaborative Projects
An essential aspect of handicrafts is their capacity to foster community connections. Collaborative projects involving multiple artisans can amplify sustainable practices while creating a network of support and resource-sharing. Initiatives like community craft fairs or workshops allow not only for knowledge exchange but also the pooling of resources, resulting in more sustainable production methods. Participating in such events often leads to increased visibility and new opportunities for small craftsmen.
Moreover, these collaborations can promote cultural exchange and innovation, leading to the creation of hybrid crafts that reflect both traditional techniques and contemporary trends. By embracing this blend of old and new, artisans continue to captivate modern consumers while retaining a strong connection to their roots. In states such as California and New Mexico, craft cooperatives are forming to showcase the amalgamation of diverse cultural influences, further enriching the handicraft landscape.
Awareness as a Driving Force for Change
As consumers become more informed about the implications of their buying choices, the demand for greater transparency in the supply chains of handicrafts also rises. Today’s consumers are advocating for brands that prioritize ethics, sustainability, and community engagement. The trend of ethical consumerism is reshaping the market and encouraging handicraft producers to adopt more sustainable practices.
Furthermore, social media platforms provide artisans with tools to share their stories, enabling a direct connection with consumers. This relationship fosters greater appreciation for the craftsmanship involved, encouraging individuals to invest in handmade goods. As a result, artisans can communicate not only the aesthetic value of their products but also the emotional stories and cultural significance behind them.
In light of these developments, the future of handicrafts appears promising. By emphasizing sustainability, cultural preservation, and economic empowerment, artisans are redefining what it means to engage with our environment while creating beautiful, meaningful work. This vibrant movement not only breathes life into local economies but also instills a deeper respect for the artisanal heritage in the hearts of consumers.
DISCOVER MORE: Click here to uncover the emotional and mental benefits of photography therapy
Conclusion: The Future of Handicrafts in Sustainable Practices
The journey through the impact of handicrafts on sustainability reveals a rich tapestry woven with threads of cultural preservation, economic empowerment, and community connection. Artisans, who embody age-old skills, are not just creating products; they are nurturing identities and fostering traditions that might otherwise be lost in a rapidly globalizing world. As the demand for ethical and sustainable goods continues to rise, these craftsmen stand at the forefront, redefining consumer culture from simply transactional to profoundly transformative.
Recent trends indicate that consumer preferences are increasingly leaning toward support for local artisans and their practices, reflecting a deepening awareness of social and environmental responsibility. The global handicrafts market, projected to reach new heights, showcases the blending of traditional craftsmanship with modern sustainability practices. Initiatives aimed at promoting cooperative models are revolutionizing the local economies, providing indispensable financial independence to artisans and empowering communities in the process.
Looking ahead, it is essential to recognize that the revival of handicrafts is both a response to and a catalyst for change in consumer behavior. By choosing handmade, sustainable goods, individuals can foster a deeper connection to cultural narratives and advocate for fair labor practices. This movement is not merely about preserving the past; it is about shaping a sustainable future that honors heritage while inviting innovation. As we continue to embrace this intersection of creativity and awareness, we may very well find that the art of creation holds the key to sustainable living.